The peak of Emotet detections, in March, is pointed out as the main responsible for the increase in threats via email, including in Europe.
Email threats worsened in the first four months of 2022 (or Q1 2022), growing 37% compared to the last four months of 2021 (or Q3 2021). The conclusion is from ESET Threat Report T1 2022, which compiles key statistics from ESET’s detection systems, highlighting notable examples of its cybersecurity research and revealing insights exclusive on current threats and trends for the future.
Threats via email
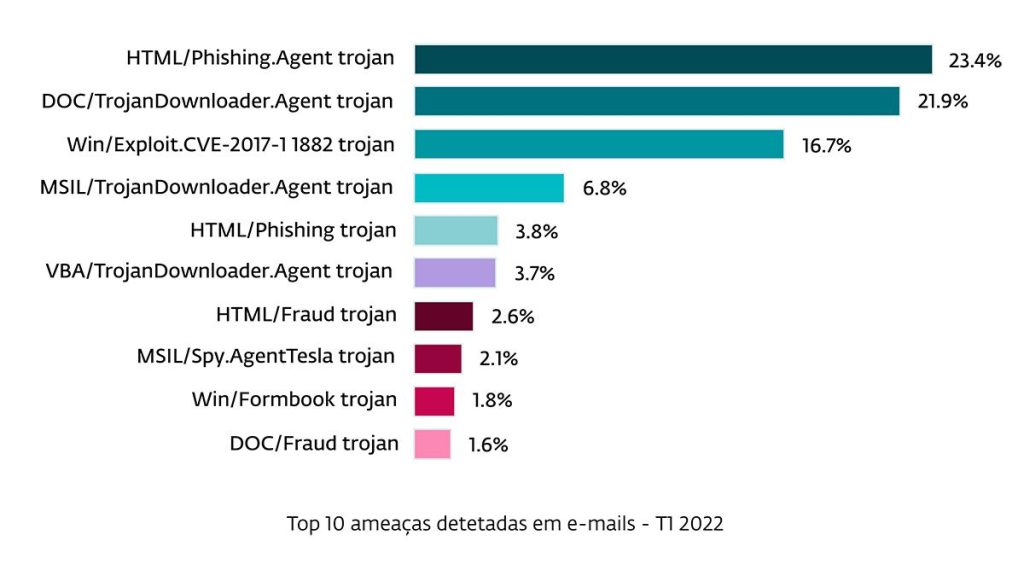
Despite active phishing activities, it was email spam campaigns, with malicious documents from the Emotet banking trojan family, that are cited as the main reason for the growth of email threats. In March 2022, ESET saw a spike in large-scale Emotet email campaigns, detected as variants of DOC/TrojanDownloader.Agent. This increase was also registered in Europe, and corresponds to some of the 10 main threats detected in the country in the first four months of the year.
Globally, the incidence of DOC/TrojanDownloader.Agent in mailboxes was such that ESET recorded an increase of 829% compared to variant detections in Q3 2021. DOC/TrojanDownloader.Agent represents Microsoft Word documents malicious programs that download other malware onto the Internet.
The countries most affected by the renewed Emotet campaigns were Japan, Italy and Spain. However, this campaign preceded Microsoft’s decision to disable Visual Basics for Applications macros downloaded by default in Office programs – one of the main distribution routes used by Emotet. That is, in the future, the operators of this family of trojans will be forced to look for new avenues of attack.
Another threat distributed as email attachments – and Discord – with substantial growth in Q1 2022 was MSIL/TrojanDownloader.Agent, which grew by 130% compared to Q3 2021. This malware attempts to download other malware via various methods, typically containing a URL or a list of URLs leading to the final payload.
MSIL/TrojanDownloader.Agent was the third biggest threat detected in Q1 2022. Among the types of malicious attachments distributed via email in Q1 2022, more than half were Windows executable attachments (55%). Script files (30%) and Office documents (10%) were also popular with cybercriminals. The prevalence of Office files has doubled in this period due to Emotet activity, but is expected to decrease in the future due to the blockage of the distribution route.